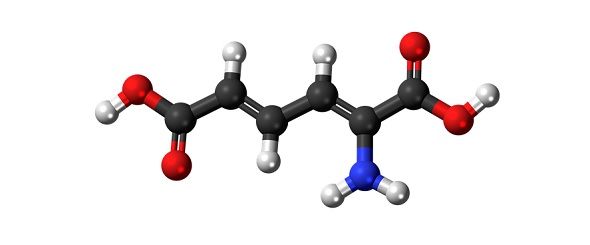
When chemical bonds join any atoms (two or more) together they are known as molecule. But such molecules consisting of different atoms (two or more) of different chemical elements are called compounds. However, it is a fact that all compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
So, we can say that any combination of atoms is a molecule, but when the combination of atoms is of different elements, it is known as a compound. Let’s take a example to understand in a better way, how the gas Hydrogen (H2), the Oxygen (O2), water (H2O), HCl, Ozone (O3), etc. are molecules, since they have two or more atoms. On the other hand, carbonate of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), NaCl, H2O, etc. are compounds as they are made up of different elements with different atoms.
Secondly, molecules are determined by the number of atoms involved in the chemical bond, but compounds are determined by the types of bonds they share between atoms, which can be covalent, metallic or ionic.
Covalent bonds are those types of chemical bonds, in which atoms share electrons as in O2 (oxygen molecule). But the ionic or electrovalent bonds are bonds in which an atom donates its electrons to another atom, as in NaCl. The bond that is shared between two metal atoms is known as a metallic bonding.
Therefore, we can say that the atoms play the main role in chemistry, as they are the smallest unit of matter, but when combined with other atoms they can give rise to different elements and compounds.
However, there are many things to discuss, but in this article we will discover the differences between two closely related and confusing terms, which are molecules and compounds.
Comparison chart
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | MOLECULES | COMPOUNDS |
|---|---|---|
| Sense | When two or more atoms are chemically bonded together it is known as a molecule. | When two or more different elements are chemically bonded together, it is known as a compound. |
| Properties | Molecules can be heteronuclear or homonuclear. | As the compound is in physical form, they are always stable. |
| Molecules can be unstable. | Compounds are made up of different elements. | |
| types of bonds | It has ionic or covalent bonds. | Has ionic, metallic or covalent bonds. |
| Examples | Ozone (O3), Oxygen (O2), Dinitrogen (N2), water (H2O), etc. | Calcium carbonate (CaCO3), calcium chloride (CaCO3), chloride (CaCO3), chloride of sodium chloride (NaCl), nitric acid (HNO3), etc. |
Definition of molecules
When two or more atoms join together to form the recognisable unit, in which the pure substance will be able to retain its chemical properties and composition even after the unit is split, it is known as a molecule.
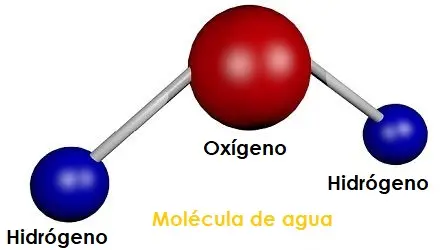
Molecules can consist of atoms of the same element, or they can be of different chemical elements. If it contains atoms of the same chemical element, it is known as homonuclear as in the oxygen (O2) molecule. But if the molecule is composed of different atoms and elements, it is known as heteronuclear as in water (H2O).
Types of molecules
Diatomic, triatomic, polyatomic molecules.based on the number of atoms per molecule.
fHomonuclear, HeteronuclearHomonuclear: Molecules containing atoms of the same element are homonuclear, whereas molecules containing atoms of different chemical elements are homonuclear.
Organic and inorganic moleculesOrganic molecules: Molecules that are composed of C, H elements with the addition of other elements are organic molecules, while molecules with different combinations of elements are inorganic molecules.
Covalent ionic molecule: Molecules based on the bond they share, which can be covalent or ionic.
Examples: HCl, CO2, H3+,NaCl, NO2, P4, PCl5, C6H12O6, etc.
Definition of compounds
A group of different atoms and different elements bonded together by chemical bonding is known as a compound. The chemical bond can be covalent, ionic or metallic.
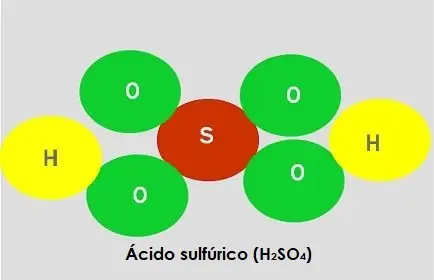
As stated above, all compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
Types of compounds
Diatomic, Triatomic, PolyatomicCompounds that vary according to the number of atoms present.
Simple and complex compoundsCompounds are differentiated according to their complexity.
Organic and inorganic compounds: On the basis of compounds, such as carboxylic acids, amines, alcohols, hydrocarbons, amides, etc., fall into the organic compound. Nitrites, nitrates, hydrides, oxides, carbonates, halides, etc. belong to inorganic compounds.
Covalent and ionic compounds: the differentiation is based on covalent bonds or ionic bonds.
An important point to consider is that only heteronuclear molecules are classified as compounds, but not homonuclear molecules.
Examples: acetic acid (C2H4O2), alcohol (C2H6O), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), H2O, NaCl, etc.
The compounds are presented by their chemical formula. For example, H2O is the chemical formula for water, which shows that the compound has two hydrogen molecules with one oxygen molecule.
Key differences between molecules and compounds
The following are critical for identifying the differences between molecules and compound:
- When two or more atoms are chemically bonded together it is known as a molecule. On the other hand, when two or more different elements with different atoms are chemically bonded together, it is known as the compound.
- Molecules can be heteronuclear or homonuclear and are unstable; however, compounds are heteronuclear molecules and are always stable as they are in physical form.
- Molecules can have ionic or covalent bonds, while compounds have ionic, metallic or covalent bonds.
- Ozone (O3), oxygen (O2), dinitrogen (N2), water (H2O) etc., are examples of molecules, while calcium carbonate (CaCO3), sodium chloride (NaCl), nitric acid (HNO3), etc., are examples of compounds.
Conclusion differences between molecules and compounds
Molecules and compounds are the most commonly used terms in the field of chemistry. This article was presented to discuss the essential differences between the two words i.e. molecules and compounds in the comparison table and also with the help of critical differences. This may help the reader to understand the concept more clearly.