We can divide the ecosystem into two main categories: abiotic y biotics, according to whether they are living or non-living. Our ecosystem acts as a platform that portrays the interaction between living and non-living organisms. biotic factors and abiotic factors.
Biotic factors include the living components that can grow, survive and adapt. Whereas abiotic factors are simply the non-living elements of the environment. They tend to affect the rate of growth, survival and adaptation of the biotic components.
Therefore, it can be said that both factors are interconnected as the biotic factors depend on the abiotic factors to satisfy their basic needs. Similarly, abiotic components depend on biotic factors for replenishment.
We have briefly elaborated the main differences between biotic and abiotic factors in this context.
Comparative table of biotic and abiotic factors
| Basis of comparison | Abitotic factors | Biotic factors |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Abiotic factors are the non-living things in an ecosystem. | Biotic factors are the living things in an ecosystem. |
| Examples | Sunlight, temperature, energy, wind, water, soil, etc. | Plants, trees, animals, micro-organisms, etc. |
| Affects | The individual of a species determined, its populationcommunity, ecosystem and biosphere. | The biome, individual of a particular species, biosphere, population. |
| Dependence | Abiotic factors do not depend on biotic factors for their survival. | Biotic factors depend on abiotic factors for their survival. |
| Limiting factors | Due to changes in abiotic factors, the growth and development of a particular species or its population can sometimes be limited, it can sometimes hinder the entire ecosystem. |
Due to uncertain changes in particular species, they can bring about changes also in the other species, which directly or indirectly depend on them. |
| Approach to change | These factors do not adapt any change. | These factors can adapt to change in order to survive. |
What are abiotic factors?
Abiotic factors are the non-living elements of the environment. They control and affect the survival capabilities of any given organism alive.
Most of the time, they fulfil the function of agents limiting agents that regulate the growth and development of any species.
Definition of abiotic factor
“Any non-living component of the environment that directly or indirectly influences biological and ecological factors is an abiotic factor. Abiotic Factor “.
All major and minor biomes on Earth depend on some vital abiotic factors.
For example, if the temperature of a particular ecosystem rises, the rate of photosynthesis will automatically increase. This is because the enzymes involved in the reaction will work more efficiently. This increases the overall growth rate of the plants.
Also, the fauna in that region will have to spend less energy on keeping their bodies warm. This saved energy can be used even more for growth and development.
They have to invest less energy in the search for food due to the overgrowth of plants.
Categories of abiotic factors
In a broader facet, we can divide abiotic factors into three subcategories:
Climatic. These are the factors related to climate, including temperature, humidity, water availability, moisture, sunlight, wind direction/intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and the climate. carbon dioxide concentration
etc.
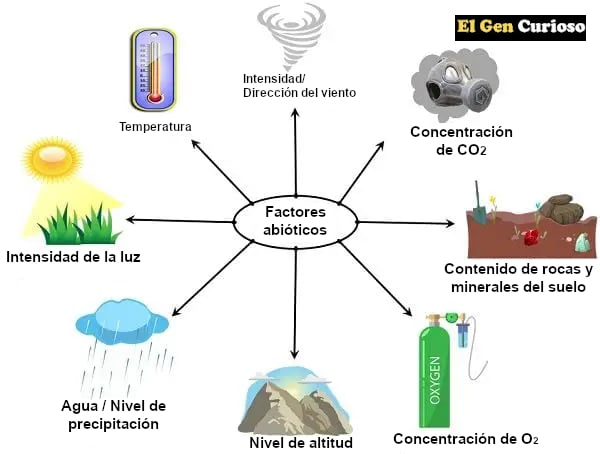
Factors vary according to the occurrence of a particular ecosystem. As the area or environment changes, so do the climatic components that influence the living entities.
For example, in an aquatic ecosystem, some important abiotic factors are:
- Water level
- Flow direction
- Water clarity
- Hydraulic pressure
- Water waves
- Exposure to sunlight
Edaphic
Edaphic relates to the land and the components associated with it. Each geographical location has a different landform and soil type that impacts the life of that region.
They involve topographical features such as:
- Soil type
- Soil nutrients
- Depressions
- Valleys
- Altitude
- Slopes
- Mineral content
Social
These are the human-induced factors such as agriculture, mining, construction, technological implementation, etc.
They never influenced the environment in earlier times and were therefore not considered the essential abiotic component. But today, they impact the flora and fauna of most of the earth’s existing ecosystems. Therefore, we can infer them as man-made abiotic components.
Abiotic resources
Abiotic components, including wind, water, sunlight, soil, etc., are all renewable resources. They help the organism to survive on earth. Humans exploit these resources for their own good. For example, water, sunlight and wind are used to produce electricity.
Understand abiotic factors with examples
Temperature: This decides the type of vegetation and wildlife at any specific location.
Take the example of a frozen tundra and a scorching desert. The tundra will have those plants and animals that can tolerate the low temperatures. While the flora and fauna of the desert region will be those that can survive the high temperatures.
SunlightFor plants, terrestrial or aquatic sunlight is needed for photosynthesis. The amount of sunlight exposure may vary from region to region.
In the same way, an animal is also influenced by exposure to the sun. For example, in aquatic ecosystems, the diversity of animals varies according to the intensity of light.
Species in the upper region, i.e. the euphotic zone, will receive the maximum solar radiation. Whereas species will differ in the twilight zone or dysphotic zone. Here, the species will get moderate light penetration. While those living in the aphotic zone are far below, where light intensity is almost zero. Here the organisms found generally lack the ability to see.
SoilSoil nutrient composition also determines the type and amount of the biotic world in a specific area.
For example, tropical forest soil is rich in nutrients and moisture content. The soil here contains abundant humus generated by dead and decaying organic debris. For this reason, there is dense and diverse plant vegetation.
In contrast, the soil in the taiga region lacks nutrients and is dry in nature. As a result, they have a limited variety of species.
What are biotic factors?
The term biotic comes from the Greek word meaning “of living things” or “of life”.
As the name suggests, this category of the ecosystem comprises living entities. They are simply any component of this earth that is alive.
Definition of biotic factors
“Any factor in the ecosystem that is alive and is shaping the ecosystem directly or indirectly affecting other organisms”.
Criteria for being a biotic factor
- For an element to be a biotic factor it must possess the following characteristics:
- They are made up of living cells.
- Ability to grow and develop.
- Ability to reproduce.
- Contains genetic material (DNA or RNA).
- Requires energy to survive.
- Response potential to a stimulus.
Components of the biotic factor
These components include the living members of the environment linked together in a food chain or web. It is based on the simple formula that one survives the other. Or it can be said that the one living species eats the lower group while the higher group of species eats it.
This food cycle comprises three main constituents:

Producers: These are generally green plants carrying chlorophyll or autotrophs. They can produce food from inorganic elements such as water, soil, sunlight, etc.
ConsumersHeterotrophs are heterotrophs that depend on producers for food. According to the complexity of food requirements and the level of cellular organisation, we divide consumers as follows:



Primary consumers or herbivoresSecondary consumers or carnivoresTertiary or omnivorous consumers
DetrivoresThey are also consumers. But they only consume dead or decaying organic matter. They survive by decomposing the nutrients left in the body after death, which is why they are also known as decomposers.
Some common examples of detritivores are earthworms, earthworms, the mushroomsdung beetles, dung beetles, millipedes, etc.

Biotic resources
These are the living, renewable resources available in the ecosystem. There is a different type of biotic resource in each and every biosphere. For example; in terrestrial biomes, these resources are
plants and plant products, including spices, timber, food, medicines, etc.
Animals and animal products such as meat, milk, eggs, wool, etc.
Decomposing organic wastes also serve as resources in the form of minerals and fuels.
Relationship between the biotic factor
Biotic factors are influenced by various phenomena such as:
- Predation by higher organisms.
- Competition for habitat, food and other resources.
- The disease burden of the smallest parasite.
- Symbiotic associations with other species.
Understand the biotic factors with an example
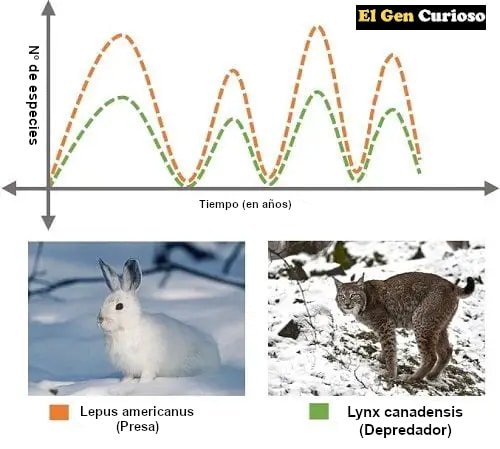
For example, let’s take the example of predation.
Canada lynx found in the Canadian and North American regions can only survive on Snowshoe rabbits. Thus, at times when the snowshoe rabbit population increases, the Canada lynx population automatically increases. Similarly, as the number of snowshoe rabbits decreases, the number of Canada lynx also decreases.
This makes it clear that the number of predators is directly proportional to the number of prey. It describes how the survival of one species depends on the other.
Key differences between abiotic and biotic factors
The following points are the key differences between abiotic and biotic factors:
- Abiotic factors are the non-living things in an ecosystem; Biotic factors comprise the living things in an ecosystem.
- Examples of abiotic factors are sunlight, temperature, energy, wind, water, soil, etc., whereas plants, trees, animals, micro-organisms, etc.
- Both (abiotic and biotic factors) can affect the individual of a particular species, its population, community, ecosystem, and the
biosphere. - Abiotic factors do not depend on biotic factors for their survival, but biotic factors depend on abiotic factors for their survival.
- Changes in abiotic factors can sometimes limit the growth and development of a particular species or its population, or can sometimes hinder the entire ecosystem. While in biotic factors due to uncertain changes in particular species, it can also cause changes in the other species, which directly or indirectly depend on them.
- Abiotic factors do not adapt to any changes, while biotic factors can slowly adapt to changes in order to survive.
Conclusion
Our biosphere consists of biome, ecosystem, community, population and species and includes all factors present on earth. Whereas ecosystems contain the synergy between non-living (abiotic) and living (biotic) factors and cover all deep areas of water, air or land.
At the same time, abiotic factors regulate the presence or survival of a particular species in that particular environment, although biotic factors depend on abiotic factors for food, protection, shelter or reproduction.